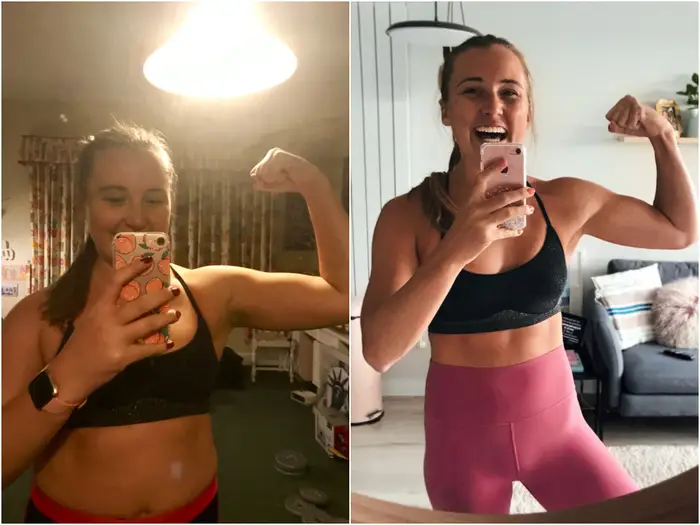
One of the most common questions in fitness is can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit. Many people assume that muscle growth only happens when you eat more calories than you burn. While this is partially true, it does not apply to every scenario. Under the right conditions, it is possible to build muscle while losing fat at the same time. This process is called body recomposition.
This article explains in detail whether can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit, how it works, who can benefit from it, the science behind it, nutrition rules, workout guidelines, mistakes to avoid, meal plans, supplements, recovery strategies, and evidence-based recommendations.
Table of Contents
What Does a Calorie Deficit Mean?
A calorie deficit is the foundation of fat loss, and understanding it is essential before answering can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit. A calorie deficit occurs when you consistently consume fewer calories than your body burns in a day. Your body needs energy to maintain basic functions—breathing, digestion, blood circulation—as well as physical activity like walking, exercising, and even sitting upright. This total daily calorie requirement is called your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE).
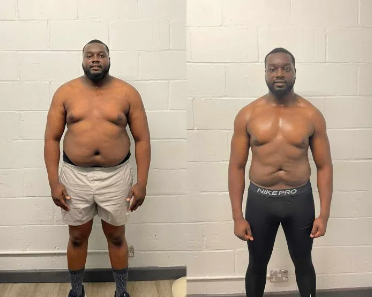
When you eat fewer calories than your TDEE, your body must look for an alternative energy source. To compensate, it begins mobilizing stored fat and converting it into usable energy. This is why a sustained calorie deficit results in fat loss.
However, what many people misunderstand is that a calorie deficit does not automatically mean muscle loss. The body can still preserve or even build muscle under the right conditions. This is where the question can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit becomes relevant. If your workouts are stimulating enough and your protein intake is sufficient, the body will prioritize repairing and growing muscle tissue while using stored fat for energy.
A calorie deficit can be created in several ways:
- Eating fewer calories
- Increasing physical activity
- A combination of both (the most effective method)
The key is maintaining a moderate deficit, typically 200–400 calories below maintenance. An overly aggressive deficit increases the risk of muscle loss and fatigue, making it harder to achieve any level of muscle growth.
In simple terms, a calorie deficit means you’re giving your body fewer calories than it needs, encouraging fat loss while—under proper training and nutrition—still allowing the possibility of muscle gain. This is the metabolic foundation behind body recomposition and helps explain why can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit is not only possible but achievable with a strategic approach.
Can You Gain Muscle in a Calorie Deficit? The Short Answer
Yes, you can gain muscle in a calorie deficit, but it depends on several factors:
- Your training experience
- Your body fat level
- Your protein intake
- Your workout program
- Your recovery quality
- Your sleep
- Your consistency
The more optimized these elements are, the better your results. However, it is much easier for some people to achieve this than others.
Who Can Gain Muscle in a Calorie Deficit?
Understanding who can gain muscle in a calorie deficit is essential to decide the right fitness plan. Below are the groups most likely to see significant results.
1. Beginners
Beginners are the most likely group to answer “yes” to can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit. When you start strength training, your body responds rapidly due to neural adaptation, increased muscle fiber activation, and the body’s ability to build lean mass while burning fat.
2. Overweight or Obese Individuals
People with high body fat levels are highly capable of gaining muscle in a calorie deficit. Their bodies have stored energy that fuels muscle growth even without extra calories from food.
This group benefits the most from body recomposition, making the question can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit much easier to answer.
3. People Returning After a Long Break
Muscle memory makes it possible to rebuild lost muscle quickly. If you were previously trained and took a break, your muscles can grow even when you are in a calorie deficit. This is another strong case for can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit.
4. Steroid Users
Though not recommended, anabolic steroid users can gain muscle under any calorie condition. They are included here because they are a scientific example of extreme muscle retention and growth.
But for natural lifters, the question can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit requires strategic training and nutrition.
Who Has Difficulty Gaining Muscle in a Calorie Deficit?

Not everyone can easily build muscle in a calorie deficit. The following individuals may find it harder:
- Advanced lifters
- People with already low body fat
- Individuals lacking protein
- Lifters without progressive overload
- People with poor sleep
- Individuals under extreme deficits
These groups may have slower results, but they can still achieve recomposition with perfect execution.
The Science Behind Gaining Muscle in a Calorie Deficit
Understanding the science behind whether can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit requires a closer look at how the body builds, maintains, and breaks down muscle. Traditionally, fitness experts believed that muscle growth could only happen in a calorie surplus because building new tissue requires energy. But modern research shows this is not entirely true. Under the right internal conditions, the body can build muscle even when total calorie intake is below maintenance.
To fully understand this phenomenon, we must explore how muscle protein synthesis works, how the body uses stored energy, the role of hormones, and how training affects muscle adaptation.
1. Muscle Protein Synthesis vs. Muscle Protein Breakdown
Your ability to answer can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit depends on the relationship between:
- Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS) – the process of building muscle
- Muscle Protein Breakdown (MPB) – the process of degrading muscle
You gain muscle when MPS > MPB.
Even in a calorie deficit, if your protein intake is high and your workouts stimulate strong MPS, the body can still shift toward building muscle. Studies show that resistance training triggers a spike in muscle protein synthesis that can last 24–72 hours.
This means that even with fewer calories, your body can build new muscle tissue as long as:
- You provide enough protein
- You apply progressive overload
- You recover properly
This explains why the answer to can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit is often yes.
2. Your Body Uses Stored Energy to Build Muscle
The body does not rely solely on calorie intake to fuel muscle growth; it also uses stored body fat.
When you are in a calorie deficit, your body breaks down fat stores to produce energy. This energy can support:
- Strength training
- Recovery processes
- Repairing and building muscle fibers
This is why overweight or obese individuals can strongly benefit from recomposition. They have more stored energy, making it easier to answer can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit with a confident yes.
3. Hormonal Environment Supports Recomposition
Hormones play a crucial role in whether can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit. Some of the key hormones include:
1. Insulin
Insulin helps transport nutrients into muscle cells. In a calorie deficit, insulin levels drop, but this actually increases fat oxidation. When paired with protein-rich meals, insulin spikes just enough to support muscle growth without promoting fat storage.
2. Testosterone
Strength training boosts testosterone levels, even during a calorie deficit. Testosterone directly increases muscle protein synthesis.
3. Growth Hormone
Calorie deficit increases growth hormone, especially during fasting or sleep. GH helps burn fat while supporting lean muscle retention.
4. IGF-1 (Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1)
Stimulated by resistance training, IGF-1 helps activate satellite cells that repair and grow muscle fibers.
This combination makes body recomposition possible even with lower energy intake, strengthening the case for can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit.
4. Why Progressive Overload Still Works in a Deficit
Even when calories are limited, progressive overload creates a strong enough stimulus to force the body to retain or build muscle. The body prioritizes muscle preservation because it interprets resistance training as a survival requirement.
This is why:
- Heavy lifting
- Training close to failure
- Increasing volume gradually
are essential in a calorie deficit. When muscle fibers are challenged, the body must repair them, and with adequate protein, this repair process often results in growth instead of loss.
5. Protein is the Key to Muscle Growth in a Calorie Deficit
Science consistently shows one thing:
High protein = higher muscle retention and growth in a deficit.
Studies demonstrate that even with a 40% calorie deficit, high protein intake can still support muscle growth during strength training.
Protein directly stimulates muscle protein synthesis, and it provides amino acids needed for rebuilding muscle tissue. This is why the focus keyword can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit is deeply connected to protein intake. Without sufficient protein, the answer becomes “no.”
6. Strength Training Improves Nutrient Partitioning
Nutrient partitioning refers to how the body directs calories—either toward:
- muscle, or
- fat
When you perform resistance training, the body becomes more efficient at shuttling nutrients toward muscle repair instead of fat storage. This enhances your ability to build or maintain muscle even with limited calories.
This explains why lifting weights increases the likelihood that can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit is achievable.
7. Muscle Memory Helps Returning Lifters
If you have trained before, your muscle cells contain “myonuclei”—tiny structures that remain even after muscle shrinkage. They allow your muscles to grow rapidly once you start training again, even without a calorie surplus.
This is why people returning to training often see rapid results in a deficit.
8. Increased Fat Oxidation Supports Muscle Growth
A calorie deficit increases fat oxidation. When body fat is used as energy, the body conserves muscle tissue because:
- Fat becomes the primary energy source
- Muscle breakdown is reduced
- More energy becomes available for recovery
This metabolic shift supports the idea that can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit is realistic under the right conditions.
Protein Intake: The Most Important Factor
When asking if can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit, protein is the most important nutritional element.
Optimal Protein Intake:
1.6 to 2.4 grams of protein per kg of body weight.
Why High Protein Works:
- Boosts muscle protein synthesis
- Reduces muscle loss
- Keeps you full
- Improves fat loss
- Supports recovery
If you want to maximize your chances of achieving muscle growth while in a deficit, protein must be your priority.
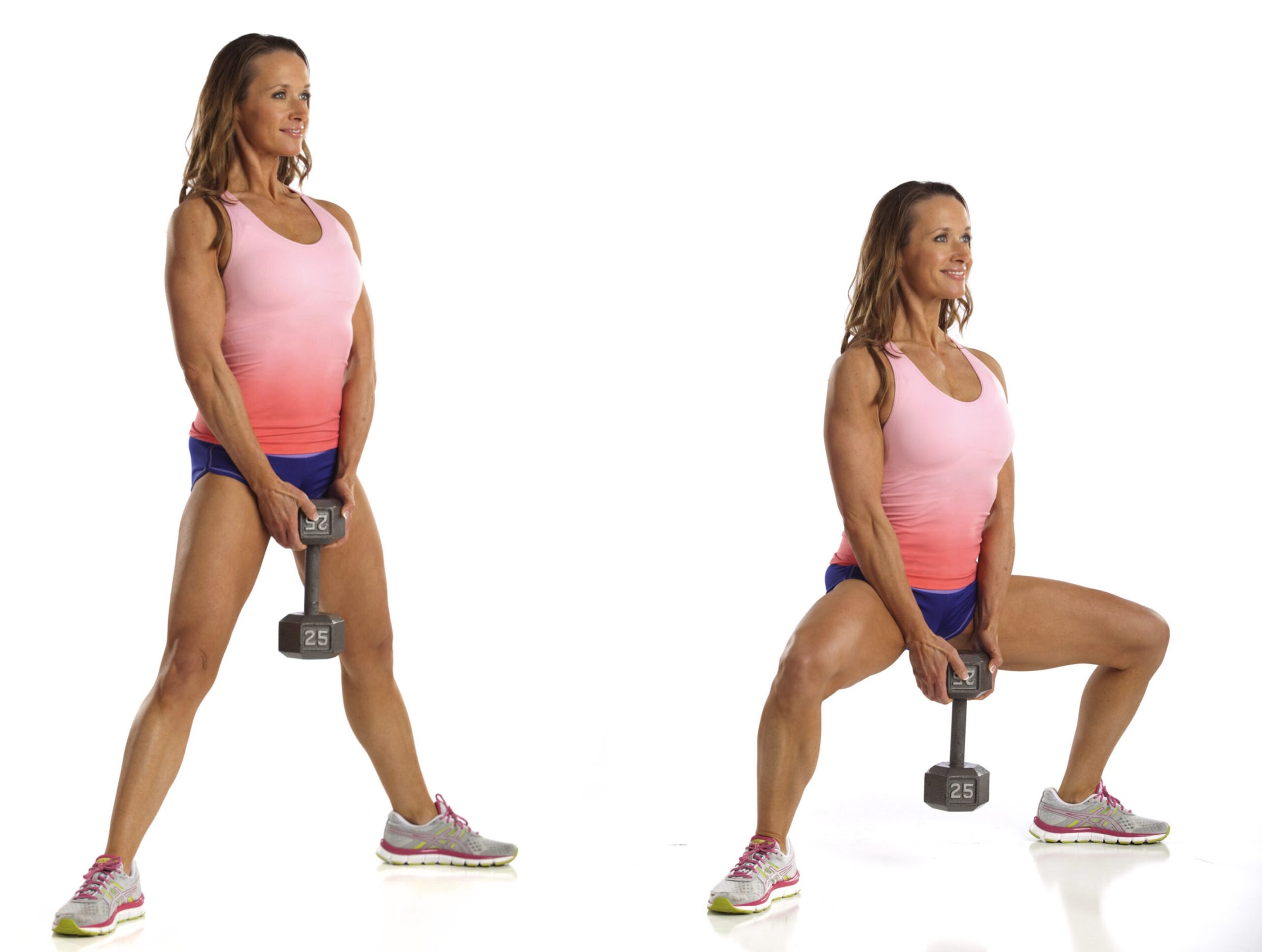
How to Train for Muscle Gain in a Calorie Deficit
Training is crucial in answering can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit. You must train smart, not just hard.
1. Focus on Strength Training
Strength training is essential. Lifting heavy weights signals the body to build muscle. Without this, the answer to can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit becomes “unlikely.”
2. Use Progressive Overload
Your workouts must get harder over time. Increase:
- Weight
- Sets
- Reps
- Frequency
- Time under tension
This pushes the body to build new muscle.
3. Limit Excessive Cardio
Too much cardio causes muscle loss in a calorie deficit. Light to moderate cardio is acceptable. But your main priority is weight training.
4. Train Big Muscle Groups
To maximize results in a calorie deficit, focus on compound exercises:
- Squats
- Deadlifts
- Bench press
- Rows
- Pull-ups
- Overhead press
These build maximum muscle with minimal calorie intake.
5. Full Body or Upper/Lower Split
Training 3 to 5 days per week works best. This increases muscle protein synthesis frequency.
Sample Workout Plan (Optimized for Calorie Deficit)
Day 1: Upper Body
- Bench press
- Bent-over row
- Shoulder press
- Lat pulldown
- Tricep dip
- Bicep curls
Day 2: Lower Body
- Squats
- Deadlifts
- Leg press
- Lunges
- Hamstring curls
- Calf raises
Day 3: Full Body
- Deadlift variation
- Pull-ups
- Bench press
- Hip thrust
- Row machine
This routine helps maximize your chances of achieving results when asking if can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit.
Nutrition Strategy for Muscle Gain in a Calorie Deficit
To answer can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit, you need a structured nutrition plan.
1. Keep the Deficit Moderate
A 200–300 calorie deficit is ideal. Excessive deficits cause muscle breakdown.
2. Eat High Protein
Every meal should include protein:
- Chicken
- Eggs
- Fish
- Lean beef
- Greek yogurt
- Protein shake
3. Choose High-Volume Foods
This helps control hunger:
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Beans
- Whole grains
4. Track Calories and Macros
Without tracking, the question can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit becomes harder to answer confidently.
5. Include Pre- and Post-Workout Nutrition


Carbs and protein improve training performance.
Supplements That Help Muscle Gain in a Calorie Deficit
Supplements are optional, but they help support your ability to gain muscle in a calorie deficit.
Recommended:
- Whey protein
- Creatine
- Omega-3
- Vitamin D
- BCAAs (optional)
- Caffeine
Creatine is especially useful because it boosts strength even in a calorie deficit.
Common Mistakes That Prevent Muscle Gains in a Calorie Deficit
If you’re still unsure about can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit, avoid these mistakes:
- Deficit too large
- Not enough protein
- Too much cardio
- No progressive overload
- Poor sleep
- Training too frequently
- No rest days
Correcting these issues significantly increases your chance of success.
Realistic Expectations: How Much Muscle Can You Gain?
Most people can gain:
- Beginners: 1–2 kg per month
- Intermediates: 0.25–1 kg per month
- Advanced: minimal
This demonstrates that the answer to can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit is yes, but results vary by experience level.
Signs You Are Gaining Muscle in a Deficit
You may be successfully achieving recomposition if you notice:
- Increased strength
- Better muscle definition
- Reduced waist size
- Stable body weight with better shape
- Higher energy levels
These are clear indicators supporting can you gain muscle in a calorie deficit.
FAQ: Can You Gain Muscle in a Calorie Deficit?
1. Is it really possible to gain muscle while losing fat?
Yes. Under the right conditions, you can gain muscle in a calorie deficit through progressive overload, high protein intake, and smart recovery.
2. How much protein do I need daily?
1.6–2.4 g per kg of body weight.
3. Do beginners gain muscle in a deficit faster?
Yes. Beginners have the best chance due to rapid adaptation.
4. How long does body recomposition take?
6–12 weeks for noticeable results.
5. Should I avoid cardio completely?
No, but limit excessive cardio. Focus on strength training.
6. What is the best workout split for a deficit?
Full body or upper/lower split 3–5 days per week.
7. Should I take creatine in a calorie deficit?
Yes. Creatine helps maintain strength and muscle mass.
8. Do I need supplements?
Not required, but they help support performance.




