Building strong, powerful, and defined quadriceps is one of the most important goals in lower-body training. The quads play a major role in walking, running, jumping, squatting, and maintaining stability throughout the entire body. While machines and barbells are helpful, dumbbell quad exercises are often the most accessible, versatile, and effective option for beginners, intermediates, and even advanced lifters. With just a pair of dumbbells, you can build size, strength, and muscular balance without needing a full gym.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Quadriceps Muscles
The quadriceps, often referred to simply as the “quads,” are one of the most important and powerful muscle groups in the lower body. For anyone performing dumbbell quad exercises, understanding how the quadriceps work is essential for maximizing strength, ensuring proper form, and preventing injury. The quads play a central role in almost every daily movement—from walking and climbing stairs to running, jumping, and maintaining posture. This section explores their anatomy, functions, and importance in lower-body training.
Anatomy of the Quadriceps
The quadriceps consist of four major muscles, located at the front of the thigh:
- Vastus Lateralis – The largest part of the quad, located on the outer side of the thigh. It is especially active during movements like squats and lunges.
- Vastus Medialis – Located on the inner part of the thigh, this muscle contributes heavily to knee stability. The teardrop-shaped portion near the knee is part of the vastus medialis.
- Vastus Intermedius – Positioned deep between the vastus lateralis and medialis, it assists with overall thigh strength and knee extension.
- Rectus Femoris – The only quad muscle that crosses both the hip and knee joints, making it responsible for both hip flexion and knee extension. It is heavily engaged in exercises involving lifting the thigh or kicking motions.

Understanding these muscles is crucial because different dumbbell quad exercises activate each part of the quadriceps in unique ways. For example, front-loaded exercises tend to target the rectus femoris more, while wider stances can emphasize the vastus lateralis.
What Do the Quadriceps Do?
The primary role of the quadriceps is knee extension—straightening the leg at the knee joint. This function is vital for:
- Standing up from a sitting position
- Walking and running
- Jumping and landing
- Stabilizing the knee joint during movement
Additionally, because the rectus femoris also crosses the hip joint, the quads assist with hip flexion, making them essential for:
- Climbing stairs
- High-knee movements
- Sprinting
- Lifting the thigh during sports
When you perform dumbbell quad exercises, you are essentially strengthening the muscles that support these basic but important actions.
Importance of Quadriceps Strength
Strong quadriceps contribute significantly to overall lower-body performance. Here’s why they matter:
- Improved Knee Health: Weak quads are linked to knee pain, instability, and higher injury risk. Strengthening them helps maintain smooth knee movement and supports ligaments.
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: Powerful quads improve sprinting speed, jumping power, balance, and agility.
- Better Posture and Mobility: Since the quads contribute to hip and knee alignment, strong quads help prevent lower-body imbalances and improve posture.
- Injury Prevention: Strong quads protect the knee joint and reduce stress during movements like running or lifting weights.
- Daily Functional Strength: Activities such as standing, squatting, lifting objects, and climbing stairs heavily rely on the quadriceps.
How Dumbbells Target the Quadriceps
Dumbbells are highly effective for quad training because they allow controlled, isolated loading. Whether performing dumbbell squats, lunges, step-ups, Bulgarian split squats, or goblet variations, dumbbells allow:
- Greater range of motion, which activates the quads more deeply
- Improved muscle symmetry, since each leg must work independently during certain exercises
- Progressive overload—easily increasing weight as strength improves
- Enhanced balance and stabilization, leading to better functional strength
Because dumbbells can be held in different positions (goblet, front-rack, suitcase hold), they can shift tension across the quadriceps muscles, creating more targeted and effective quad activation.
Quad Activation in Different Movements
Different movements emphasize different portions of the quads:
- Goblet squats target the rectus femoris and vastus medialis due to upright torso positioning.
- Dumbbell lunges activate all four quad muscles intensely because of the greater knee flexion.
- Step-ups emphasize hip flexion and knee extension simultaneously, making the rectus femoris work harder.
- Bulgarian split squats create deep quad engagement, especially on the stabilizing muscles.
- Dumbbell leg extensions (if using ankle straps) specifically isolate the quadriceps, allowing a targeted contraction.
By selecting the right mix of dumbbell quad exercises, you can fully engage the entire quadriceps group and build balanced leg strength.
Benefits of Dumbbell Quad Exercises
Training the quadriceps using dumbbells offers a combination of versatility, efficiency, and functional strength-building that many other training tools cannot match. While barbells and machines are widely used for leg training, dumbbell quad exercises provide unique advantages that improve muscle balance, stability, mobility, and overall athletic performance. This section explores the most important benefits in depth so readers understand why dumbbells should be a central component of lower-body training.
- Improves Quadriceps Strength and Size
One of the primary benefits of dumbbell quad exercises is their ability to build significant strength and hypertrophy in the quadriceps muscles. Because dumbbells allow full range of motion and deep knee flexion, they recruit a high level of muscle fibers. Exercises such as dumbbell squats, lunges, goblet squats, and Bulgarian split squats provide constant resistance that stimulates muscle growth. When performed consistently with progressive overload, these exercises promote stronger, fuller, and more defined quadriceps.
- Allows Greater Range of Motion Compared to Machines
Dumbbells enable natural movement patterns that machines cannot replicate. Machines typically force the body into fixed positions, limiting motion. Dumbbells, however, move with your body, allowing deeper squats, fuller knee extension, and better hip engagement. This increased range of motion leads to improved muscle activation and better functional strength. For the quadriceps, deeper knee flexion produces more tension on the vastus medialis and rectus femoris.
- Enhances Muscle Symmetry and Corrects Imbalances
One major advantage of dumbbell quad exercises is that they force each leg to work independently during unilateral movements. Exercises like split squats, step-ups, and lunges highlight strength disparities between the right and left leg. By training each side equally, dumbbells help correct imbalances that can lead to poor posture, inefficient movement patterns, and a higher risk of injury. Balanced quad development also supports better knee alignment during daily activities and sports.
- Improves Knee Stability and Joint Health
Strong quadriceps are essential for maintaining healthy and stable knees. The quads support the knee joint through extension, absorbing shock during movement and preventing excessive strain on the ligaments. Dumbbell quad exercises encourage controlled movement, which strengthens the stabilizing muscles around the knee. Furthermore, because dumbbells allow more natural movement variations, they reduce the risk of joint compression commonly associated with rigid machine angles.
- Helps Build Functional Lower-Body Strength
Functional strength refers to the ability to perform everyday movements with ease, power, and proper mechanics. Most dumbbell quad exercises mimic real-life actions such as climbing stairs, getting up from the floor, walking uphill, carrying objects while moving, or changing direction quickly. This makes dumbbell training extremely practical for improving lower-body functional capacity. Athletes and non-athletes alike benefit from improved balance, coordination, and overall strength.
- Enhances Balance, Stability, and Coordination
Unlike machines, dumbbells require the body to stabilize itself during movement. Holding dumbbells while performing squats, lunges, or step-ups forces the core, hips, and smaller stabilizing muscles to remain engaged. This support system improves balance, enhances neuromuscular coordination, and trains the body to maintain proper alignment under load. As a result, individuals can move more confidently during both workouts and daily activities.
- Versatile and Beginner-Friendly Equipment
Dumbbells are accessible, adaptable, and beginner-friendly. They allow users to adjust weights easily, perform exercises without a spotter, and train safely at home or in the gym. Beginners often find dumbbells less intimidating than barbells, making them ideal for learning proper squat and lunge mechanics. Advanced trainees can also benefit by increasing weight, adding volume, or performing advanced unilateral variations to intensify quad training.
- Ideal for Home Workouts Without Machines
Not everyone has access to leg press machines, squat racks, or cable systems. Dumbbells offer a complete quad workout without needing bulky or expensive equipment. A pair of dumbbells enables a full range of quad-focused exercises that target all four quadriceps muscles. This makes dumbbell training an excellent option for people who train at home or travel frequently.
- Improves Athletic Performance
Athletes in sports like football, basketball, soccer, tennis, and track rely heavily on quad power for acceleration, deceleration, jumping, and lateral movement. Dumbbell quad exercises build strength in movement planes that replicate sports actions more accurately than machine-based training. Improved quad strength enhances sprinting speed, vertical jump height, cutting ability, and explosive power.
- Supports Weight Loss and Increases Calorie Burn
Leg exercises burn a high number of calories because the quadriceps are one of the largest muscle groups in the body. When you perform dumbbell quad exercises, you activate multiple muscles at the same time, significantly increasing calorie expenditure. Over time, this contributes to fat loss, better metabolic function, and improved body composition. Compound movements like goblet squats and lunges are particularly effective for boosting heart rate and promoting fat burning.
- Reduces Risk of Injury During Daily Activities
Strong quads help stabilize the knee and hip joints, reducing the likelihood of injuries such as strains, sprains, and ligament issues. Dumbbell training strengthens not only the primary quadriceps muscles but also the supporting stabilizers. Whether bending, lifting, climbing stairs, or changing direction, strong quadriceps protect the joints and promote smoother, safer movements.
- Allows Progressive Overload Without a Barbell
Progressive overload is essential for muscle growth. Dumbbells make it easy to increase resistance gradually, whether by adding more weight, increasing repetitions, or performing more challenging variations. This makes dumbbell quad exercises a safe and effective method for building lower-body strength over time without needing a heavy barbell setup.

Top 20 Dumbbell Quad Exercises (With Instructions)
The following are the most effective dumbbell quad exercises you can include in your leg workout.
1. Dumbbell Goblet Squat
One of the most powerful beginner-friendly quad builders.
How to do it:
Hold one dumbbell at chest level and squat down, keeping your torso upright.
Quad focus:
Emphasizes vastus medialis and rectus femoris.
2. Dumbbell Front Squat
Hold dumbbells on your shoulders and squat deeply.
Why it works:
It shifts more tension onto the quads than back-loaded squats.
3. Dumbbell Split Squat
A static lunge position focusing intensely on one leg at a time.
Why it works:
Increases stability and unilateral quad strength.
4. Dumbbell Bulgarian Split Squat
Place your back foot on a bench while holding dumbbells.
Quad activation:
One of the highest-activation dumbbell quad exercises ever measured.
5. Dumbbell Step-Up
Step onto a bench while holding dumbbells.
Benefits:
Enhances real-life strength patterns like climbing and running.
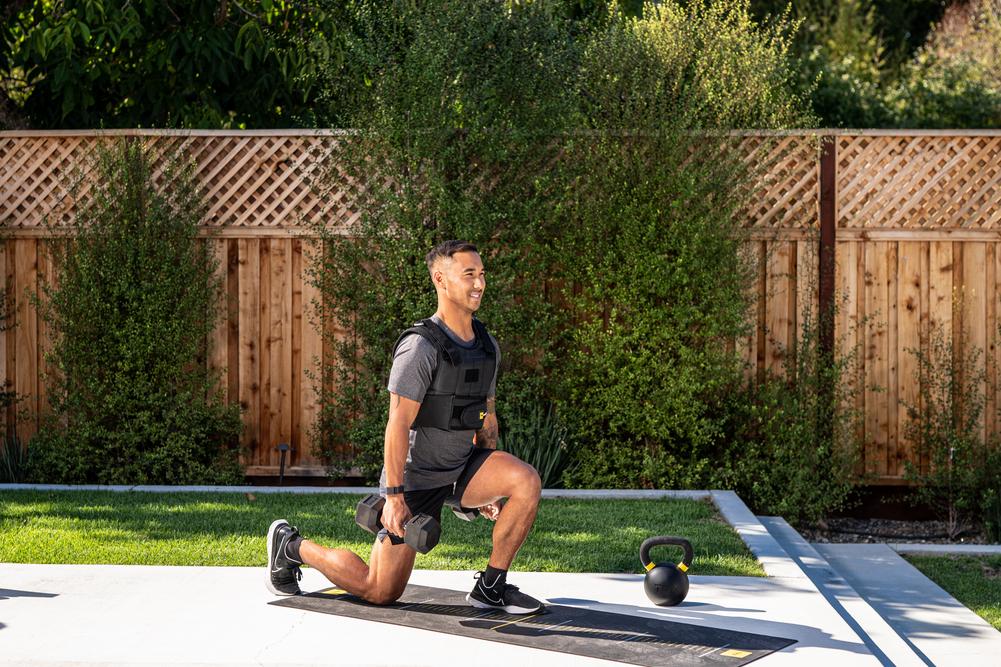
6. Dumbbell Reverse Lunge
Step backward to avoid knee strain and shift tension to the quads.
7. Dumbbell Forward Lunge
Classic movement targeting all quad heads.
8. Dumbbell Lateral Lunge
Works quads through a side-to-side motion.
9. Dumbbell Sissy Squat (Modified)
Hold dumbbells as you lean backward on your toes.
Note:
Advanced, but extremely quad-focused.
10. Dumbbell Heel-Elevated Squat
Place heels on plates or a block.
Why:
Shifts nearly all load onto the quads.
11. Dumbbell Cyclist Squat
Feet very close together, heels elevated.
Effect:
Massive quad burn due to knee flexion.
12. Dumbbell Skater Squat
Single-leg squat variation.
Focus:
Vastus lateralis and balance.
13. Dumbbell Knee Extension (Floor Variation)
A creative, home-friendly alternative to machine extensions.
14. Dumbbell Squat Jump
Explosive movement for power and athleticism.
15. Dumbbell Hack Squat (Front Hold Variant)
Hold dumbbells behind your legs.
Why:
Mimics the machine hack squat.
16. Dumbbell Curtsy Lunge
Targets inner quads and glutes.
17. Dumbbell Box Squat
Sit back on a box or bench, explode upward.
18. Dumbbell Walking Lunges
One of the best hypertrophy dumbbell quad exercises ever.
19. Dumbbell Overhead Squat
Improves mobility, core engagement, and quad activation.
20. Dumbbell Wall Sit
Quad endurance finisher. Hold dumbbells for increased tension.
4. How to Structure a Quad Workout Using Dumbbells
To maximize the benefits of dumbbell quad exercises, follow these guidelines.
Beginner Workout (30 minutes)
| Exercise | Sets | Reps | Rest | Notes |
| Goblet Squat | 3 | 10–12 | 60 sec | Keep chest up, hold dumbbell at chest |
| Dumbbell Lunges | 3 | 8 each leg | 60 sec | Step forward, maintain knee alignment |
| Dumbbell Step-Ups | 3 | 10 each leg | 60 sec | Use a stable bench or step |
| Dumbbell Leg Extension (if available) | 3 | 12–15 | 45 sec | Use ankle weights or band + dumbbell |
| Dumbbell Wall Sit Hold | 2 | 30–45 sec | 45 sec | Hold dumbbell on thighs |
| Bodyweight Squats (Finisher) | 1 | 20 | — | Burnout round for quads |
Intermediate Workout (45 minutes)
- Dumbbell Front Squat – 4×10
- Bulgarian Split Squat – 4×8 each
- Heel-Elevated Squat – 3×12
- Walking Lunges – 3×14
- Dumbbell Cyclist Squat – 3×15
Advanced Workout (60 minutes)
- Dumbbell Hack Squat – 4×10
- Bulgarian Split Squat – 4×10 each
- Dumbbell Skater Squat – 3×8 each
- Dumbbell Sissy Squat – 3×12
- Weighted Wall Sit – 60 seconds × 2
This ensures your dumbbell quad exercises routine hits all quad heads.
Training Tips for Better Quad Growth
To maximize results:
1. Use Full Range of Motion
Deeper squats activate more quadriceps fibers.
2. Keep Your Torso Upright
This shifts load from glutes to quads.
3. Elevate Heels
A proven method to isolate quads further.
4. Train Quads Twice Weekly
Optimal frequency for muscle growth.
5. Progressive Overload
Increase weight, reps, or intensity to keep building muscle.
Common Mistakes in Dumbbell Quad Exercises
Avoid these errors to stay safe and grow your quads effectively.
1. Letting Knees Collapse Inward
Leads to joint pain.
2. Leaning Too Far Forward
Shifts work to glutes instead of quads.
3. Using Too Much Weight Too Soon
Compromises form.
4. Not Controlling the Eccentric Phase
Slow lowering increases quad tension.
5. Skipping Warm-Up
A good warm-up boosts performance and prevents injury.
Variations to Increase Difficulty
When dumbbell quad exercises become too easy, progress using:
1. Pause reps
Hold the bottom position for 2 seconds.
2. Tempo reps
Lower for 3–4 seconds to increase intensity.
3. Drop sets
Lower the dumbbell weight and continue without rest.
4. One-legged progressions
Focus more tension on each individual quad.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Are dumbbell quad exercises effective for building size?
Yes. When performed with proper form and progressive overload, dumbbell quad exercises can build as much size as machine or barbell workouts.
2. Can beginners start with dumbbell quad exercises?
Absolutely. They are safe, versatile, and joint-friendly.
3. How many times a week should I train quads?
Most people benefit from 2 sessions per week of dumbbell quad exercises.
4. Can dumbbells replace barbells for leg workouts?
Yes. For many people, dumbbells provide enough resistance and range of motion to effectively grow the quads.
5. Do heel-elevated dumbbell squats really target quads more?
Yes. Elevating your heels shifts tension directly to the anterior thigh muscles, making these one of the best dumbbell quad exercises available.
6. How long until I see results?
With consistent workouts, visible changes may occur in 4–8 weeks.
Dumbbell quad exercises offer a simple, accessible, and highly effective way to build stronger, more defined quadriceps without needing a gym full of heavy equipment. With movements like goblet squats, Bulgarian split squats, heel-elevated squats, and lunges, you can create endless variations and progressions to target every part of the quadriceps.
Whether you’re a beginner training at home or an advanced lifter trying to improve leg strength and stability, incorporating dumbbell quad exercises into your leg day is one of the smartest ways to build muscle, enhance mobility, and improve overall athletic performance.

